In July 2025, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) stunned global financial markets by banning Jane Street Capital, one of the most successful and secretive trading firms in the world. The allegations? Market manipulation on an enormous scale. The outcome? Billions in gains frozen, confidence shaken, and India’s derivatives market reeling.
But what really happened? Who is Jane Street Capital? How did they pull off what SEBI calls a “sinister scheme”? And what does this mean for Indian investors?
This article dives deep into the scandal—from Jane Street’s origins to their explosive rise in India and the eventual regulatory hammer that brought them down.
🏛️ Who Is Jane Street Capital?
Jane Street is a Wall Street trading powerhouse, established in 1999. The firm operates globally with offices in New York, London, Hong Kong, and Singapore. It is known for:
- High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
- Proprietary algorithmic strategies
- Market-making across stocks, ETFs, bonds, crypto, and derivatives
With estimated annual revenues exceeding $10 billion, Jane Street is famed for its low-profile, ultra-intellectual culture. The firm employs physicists, mathematicians, and programmers who build lightning-fast trading models that capitalize on tiny inefficiencies across markets.
In India, Jane Street operated through its international arms and sub-accounts, focusing primarily on index arbitrage and derivatives trading in the NSE’s F&O segment—especially Bank Nifty and Nifty.
💡 What Did They Do?
SEBI’s investigation into Jane Street uncovered a calculated pattern of trades designed to manipulate the Bank Nifty index—one of India’s most actively traded indices—on critical monthly expiry days. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how the manipulation unfolded:
1. Initial Accumulation Phase (Morning)
Jane Street started by accumulating large long positions in select Bank Nifty constituent stocks (e.g., HDFC Bank, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank). These trades were in both the cash market and the futures market.
At the same time, Jane Street sold massive quantities of Bank Nifty call and put options—positions that would benefit if the index stayed within a narrow range or dropped sharply.
2. Artificial Pump (Midday)
Once they had built their stock positions, Jane Street aggressively pushed the prices of those banking stocks upward, causing the Bank Nifty index to rise artificially.
This pump created the illusion of strong bullish sentiment in the banking sector, attracting retail and algo-based momentum traders.
3. Sudden Dump (Afternoon)
At just the right moment, Jane Street reversed their stock trades, dumping the stocks into the open market. This abrupt selling pressure caused a sharp decline in the Bank Nifty index.
As the index fell:
- Their put options surged in value
- Their call options collapsed, benefiting them as sellers
- Retail investors, trapped at higher prices, suffered losses
This cycle was repeated on multiple expiry days, most notably January 17, 2024, and May 15, 2025.
📊 The Manipulation in Action
The following chart illustrates the price movement of the Bank Nifty index on a typical expiry day as allegedly manipulated by Jane Street:
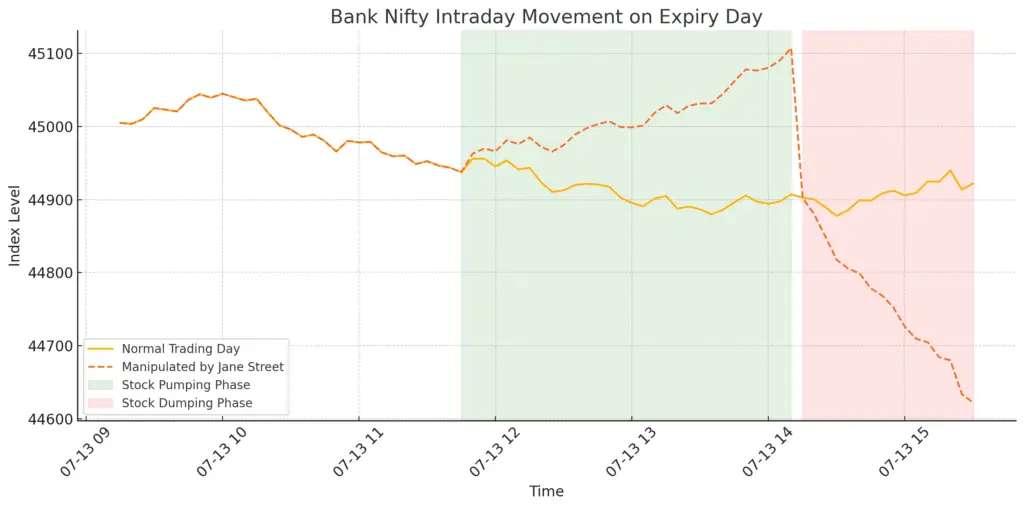
- The green area shows the “Pump Phase” where stock buying inflated the index.
- The red area represents the “Dump Phase” where heavy selling brought prices crashing down.
- The dashed line shows the manipulated path, while the solid line indicates a normal trading day.
This kind of sharp and artificial movement deviates from natural market behavior and distorts price discovery, harming retail participants and other institutions.
💰 How Much Money Did They Make?
According to SEBI and various financial estimates:
- Jane Street made over $4.3 billion (~₹35,000 crore) in India from 2023 to early 2025.
- A large portion of this came from Bank Nifty option expiry day trades.
- SEBI has frozen ₹4,800 crore (~$570 million) in alleged illegal gains.
- Their trades often accounted for 15–25% of Bank Nifty’s volume on expiry days.
This level of influence by a single firm was unprecedented and raised red flags.
🔎 Why Did SEBI Ban Jane Street?
SEBI’s interim order paints a damning picture. The core reasons behind the ban include:
1. Manipulative Trade Patterns
Jane Street’s trades in cash, futures, and options markets were not neutral. Instead, they were coordinated to manipulate the index’s expiry value.
2. False Market Signals
The firm’s strategy gave misleading price signals, drawing in unsuspecting retail traders. This violated the principles of fair market play and price discovery.
3. Harm to Retail Investors
Millions of Indian investors rely on technical charts and expiry trends. Jane Street’s actions distorted these indicators, causing real financial damage.
4. Disproportionate Position Sizes
Jane Street’s stock trades were only a fraction of their options exposure—sometimes 1:1000 leverage. They created the illusion of genuine stock activity to benefit their far larger derivatives bets.
5. Violation of Securities Law
SEBI cited violations under the SEBI (Prohibition of Fraudulent and Unfair Trade Practices) regulations, justifying the firm’s ban and fund freeze.
🧱 Legal & Market Fallout
The SEBI order is not the final verdict—it’s an interim ban pending a full investigation. However, the consequences have been immediate:
- Jane Street ceased all Indian operations temporarily.
- India’s F&O market saw a 20–21% drop in derivatives volume after the ban.
- Other foreign trading firms began reassessing their India strategies.
- Retail investors demanded greater transparency and oversight of institutional players.
Meanwhile, Jane Street has denied any wrongdoing, stating that their trades were part of legitimate arbitrage strategies that did not intend to manipulate markets.
🧭 What Happens Next?
The Jane Street case could be a watershed moment in India’s market regulation. Here’s what to expect:
🔍 1. Stricter Surveillance
SEBI is likely to increase scrutiny over high-frequency and expiry-day trades. New rules could cap position sizes or require greater transparency from foreign sub-accounts.
⚖️ 2. Legal Showdown
Jane Street may challenge the interim order in the Securities Appellate Tribunal (SAT). If SEBI wins the case, Jane Street’s Indian chapter could be permanently shut.
🧠 3. Market Education
This case highlights the importance of financial literacy. Many retail traders blindly followed index trends without understanding the forces behind them. Platforms like yours have a key role to play in bridging this gap.
🧾 Conclusion: A Cautionary Tale
Jane Street’s rise in India was nothing short of spectacular. But so was its fall.
This episode reveals how even the most sophisticated financial strategies can cross the line between smart arbitrage and market manipulation. It’s also a reminder that regulators like SEBI are increasingly watching—not just to police bad behavior, but to protect the integrity of the Indian financial ecosystem.
For investors and traders, this is a wake-up call: always question unusual market moves, understand the players behind the trades, and remember—when giants move, the ripples can drown the small.


